The National Research Institute of Maritime Cultural Heritage logo
Conservation of Metals Background Image
Conservation of Metals
Metal goods recovered from the seafloor mostly iron and bronze artifacts. Metal objects are often covered with rust, and they are frequently discovered in a shattered or dented state. Additionally, there is significant corrosion as the article was exposed to moisture and sodium for prolonged periods of time. Conservation treatment is thus conducted after removing sodium and performing stabilization treatment.
Iron relics
-
STEP 1
Preliminary investigation -
STEP 2
Cleaning -
STEP 3
Desalinization
-
STEP 4
Hardening treatment -
STEP 5
Bonding and restoration -
STEP 6
Controlling Storage environment
-
STEP 1
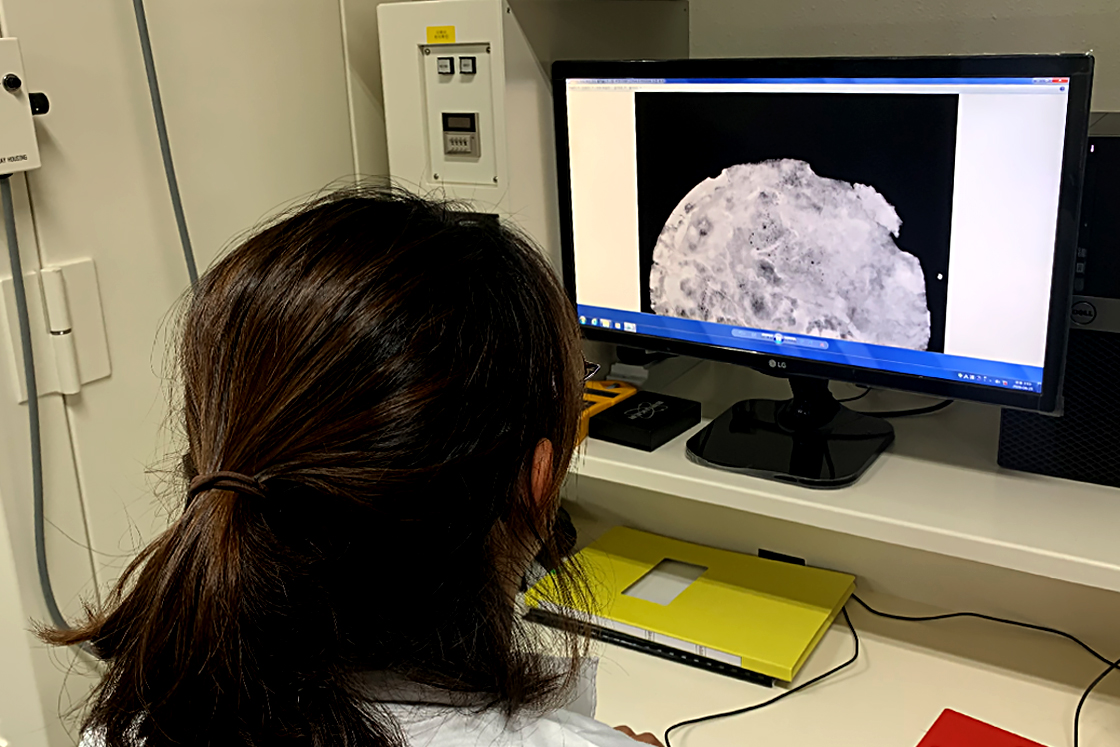
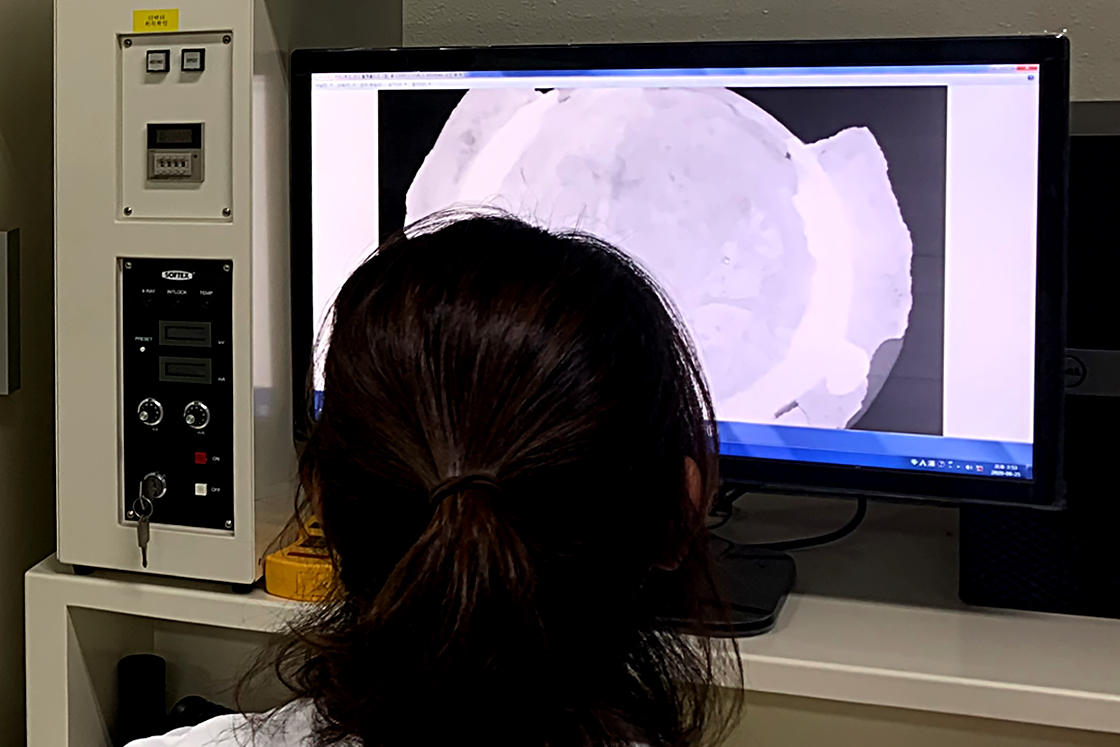
Preliminary investigation Before treating the objects, a comprehensive analysis is conducted, which is written in the artifact records card, and it is photographed and x-rayed. -
STEP 2
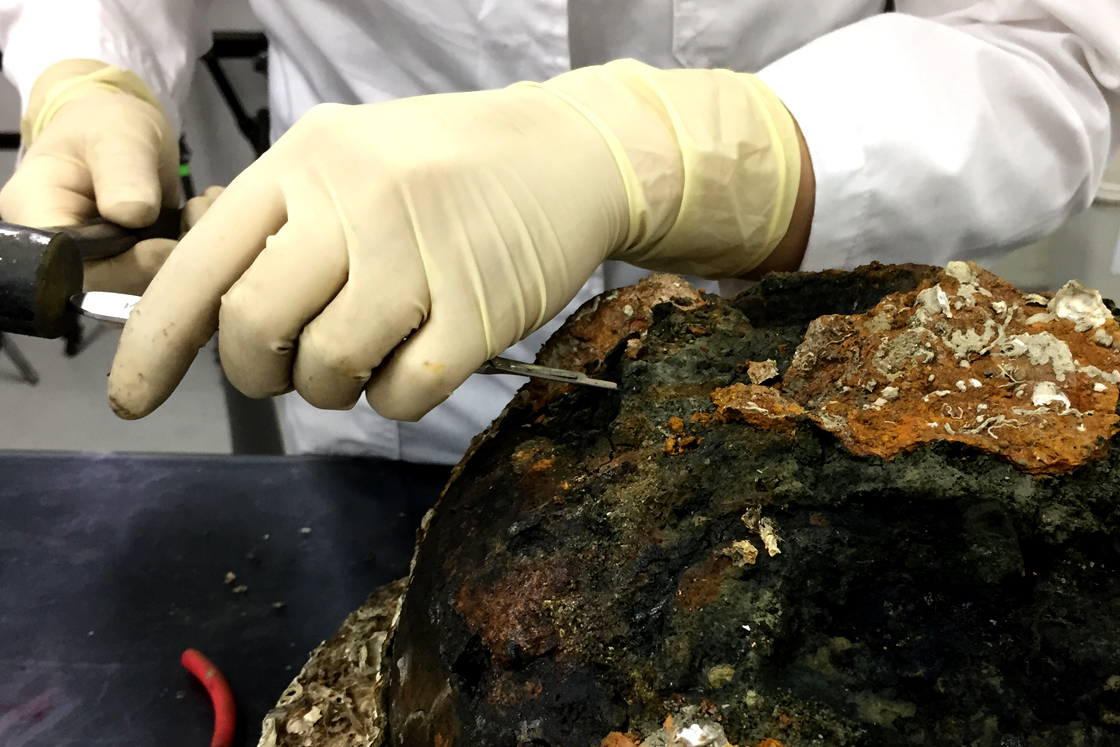
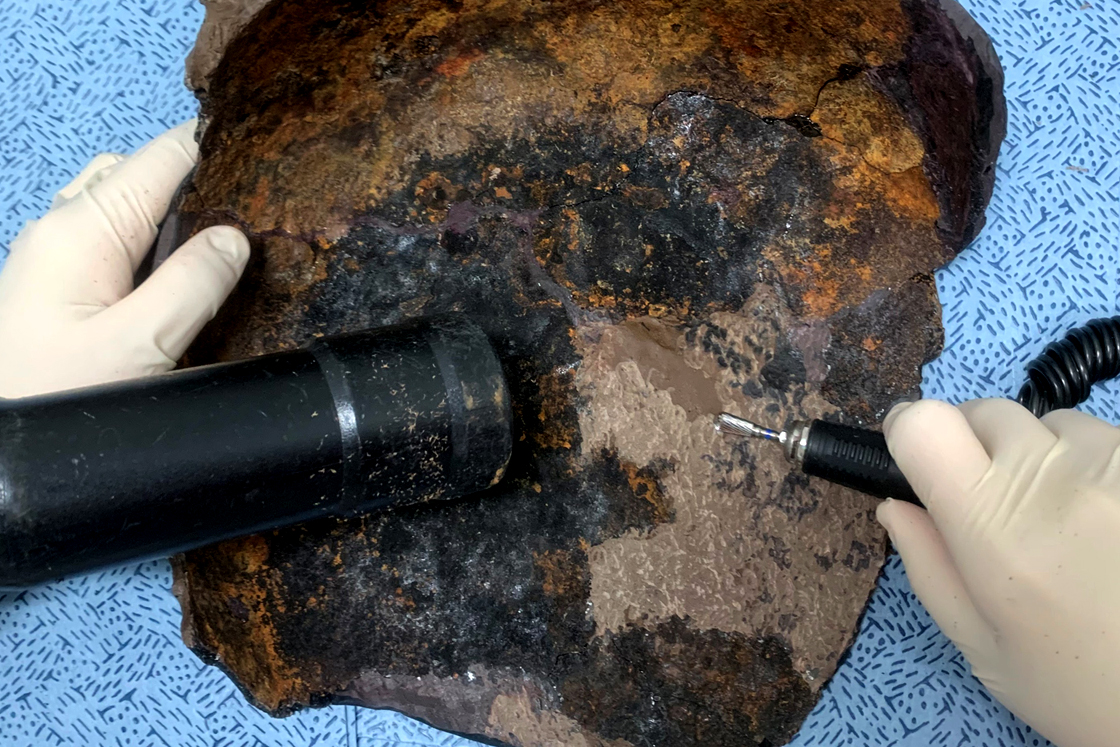
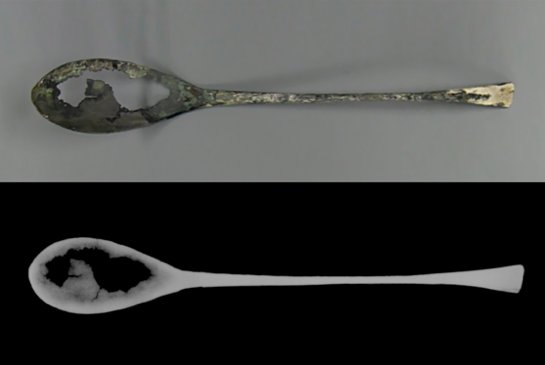
Cleaning As foreign substances are built up heavily and firmly on the objects due to the environmental condition of marshes, the activity of the sea creatures, and corrosion, the corrosion is removed using physical and chemical methods through visual and microscopic observation and reference by x-ray photographs. These materials that may cause damage to the artifact itself are not removed, and the original form of the item is maintained. -
STEP 3
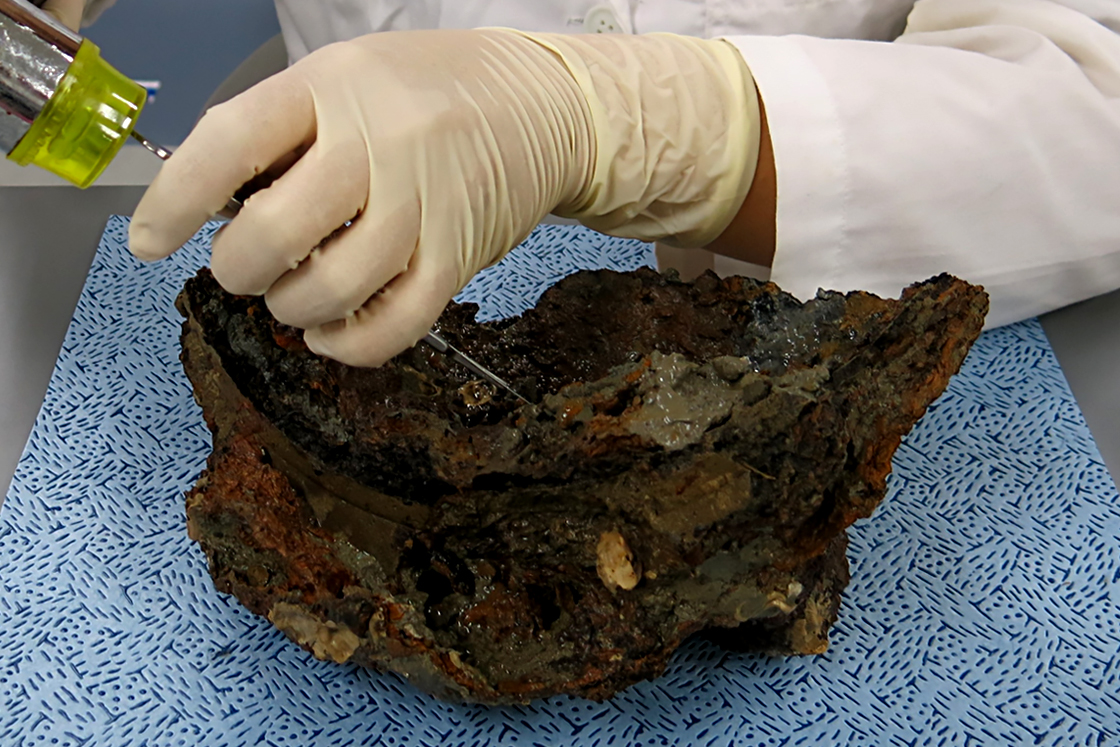
Desalinization As iron goods recovered from the seabed were exposed to sodium for prolonged periods of time, there may be recurring corrosion. Thus, in order to stabilize corrosion, corrosive factors are removed, and desalinization is conducted to prevent further corrosion. -
STEP 4
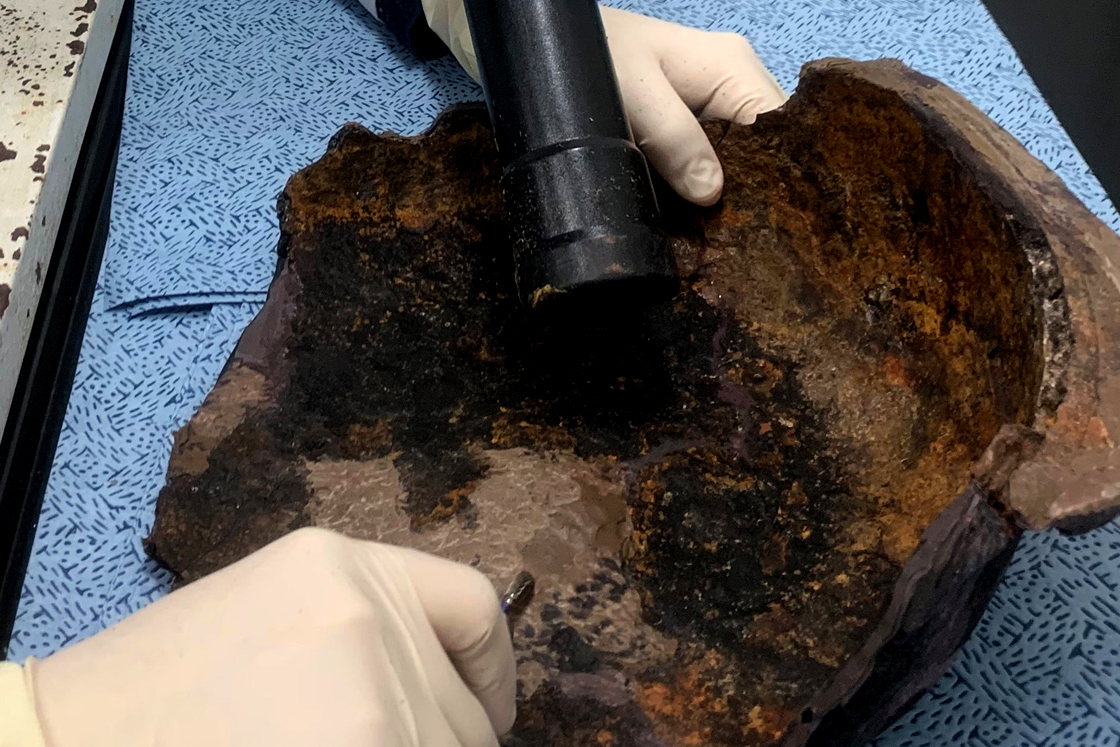
Hardening treatment As the material weakens if metals are corroded, the surface is coated in order to prevent recurring corrosion by blocking the factors of corrosion, strengthening the weakened objects that has been weakened due to corrosion. -
STEP 5
Bonding and restoration To restore the original form of the artifacts, broken parts are rejoined and missing parts are restored. -
STEP 6
Controlling storage environment A storage case was created using escal film and toilon in order to control the storage environment, and silica gel, RP-system, and a humidity instruction card were placed on the interior to enable inspection of the influx of oxygen and humidity at all times.
Bronze relics
-
STEP 1
Preliminary investigation -
STEP 2
Cleaning -
STEP 3
Desalinization
-
STEP 4
Hardening treatment -
STEP 5
Bonding and restoration -
STEP 6
Controlling storage environment
-
STEP 1
Preliminary investigation Before treating the artifact, a comprehensive analysis is conducted, which is written in the artifact records card, and it is photographed and x-rayed. -
STEP 2
Cleaning As foreign substances are built up heavily and firmly on the objects due to the environmental condition of marshes, the activity of the sea creatures, corrosion, the corrosion is removed using physical and chemical methods through visual and microscopic observation and reference by x-ray photographs. Foreign substances that may cause damage to the object itself are not removed, and the original form of the item is maintained. -
STEP 3
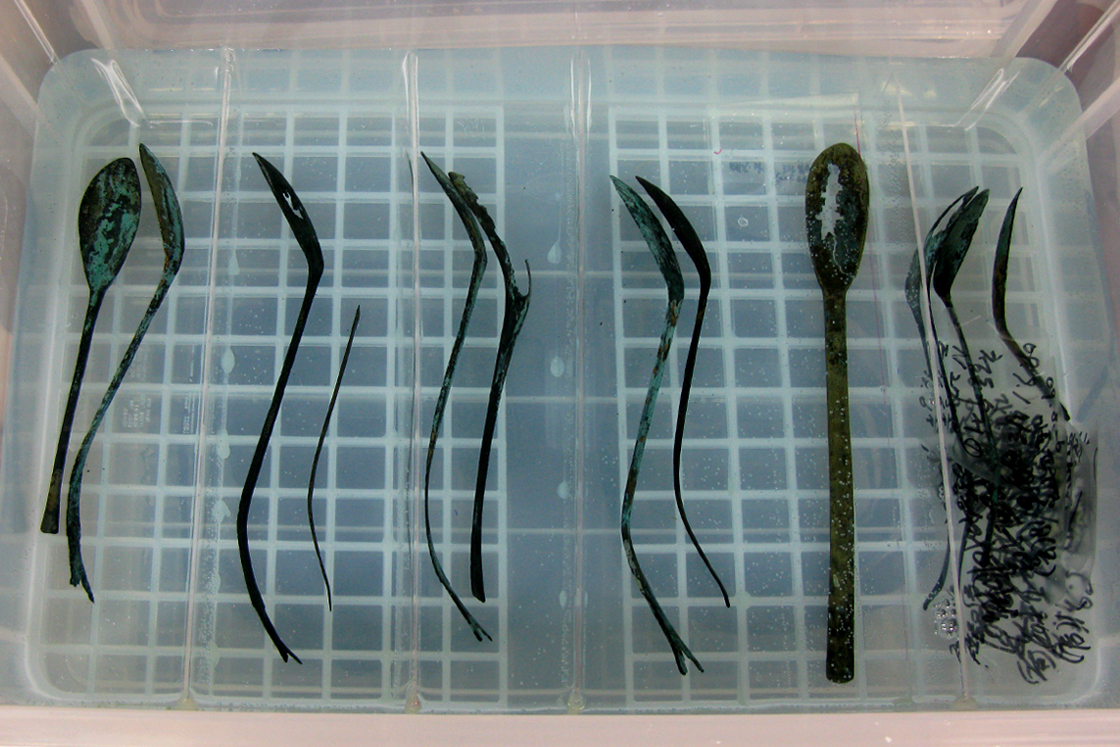
Desalinization As bronze objects recovered from the seabed were exposed to sodium for prolonged periods of time, there may be recurring corrosion. Thus, in order to stabilize corrosion, corrosive factors are removed, and desalinization is conducted to prevent further corrosion. -
STEP 4
Corrosion control and hardening treatment Bronze goods which have undergone cleaning are put through corrosion control to prevent corrosion. Afterwards, the material is strengthened and the surface is coated and put through hardening treatment in order to prevent the intrusion of corrosion factors from the outside. -
STEP 5
Bonding and restoration To restore the original form of the goods, broken parts are rejoined and missing parts are restored. -
STEP 6
Controlling Storage environment A storage case was created using escal film and toilon in order to control the storage environment, and silica gel, RP-system, and a humidity instruction card were placed on the interior to enable inspection of the influx of oxygen and humidity at all times.
-
Administrative Office Heritage Conservation and Collection Management Division
-
Contact 061-270-2090